Introduction
Polystyrene (PS) is one of the most widely used plastics in the world, found in everything from packaging materials to disposable cups. However, it also contributes significantly to global plastic pollution, as much of it is not recycled. Turning this waste into valuable products through recycling is not only an environmentally sustainable choice but also an economically beneficial practice. In this article, we will walk you through the complete process of recycling PS pellets and explore the numerous advantages of this valuable recycling practice.
The Importance of Recycling PS Pellets
Plastic pollution is one of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time. According to the United Nations, millions of tons of plastic waste end up in the oceans every year, harming wildlife and ecosystems. PS, being lightweight and widely used, is a major contributor to this pollution.
Recycling PS pellets can help mitigate these environmental issues by reducing the need for raw materials, lowering energy consumption, and reducing waste in landfills. Additionally, using recycled PS pellets instead of virgin plastic can help businesses reduce their carbon footprint, making it a key step toward sustainability.
Recycled PS pellets have a wide range of applications. They can be used in the production of packaging materials, insulation products, electronics casings, and even household items. This versatility not only promotes a circular economy but also helps to meet the growing demand for eco-friendly products.
The Complete Process of Recycling PS Pellets
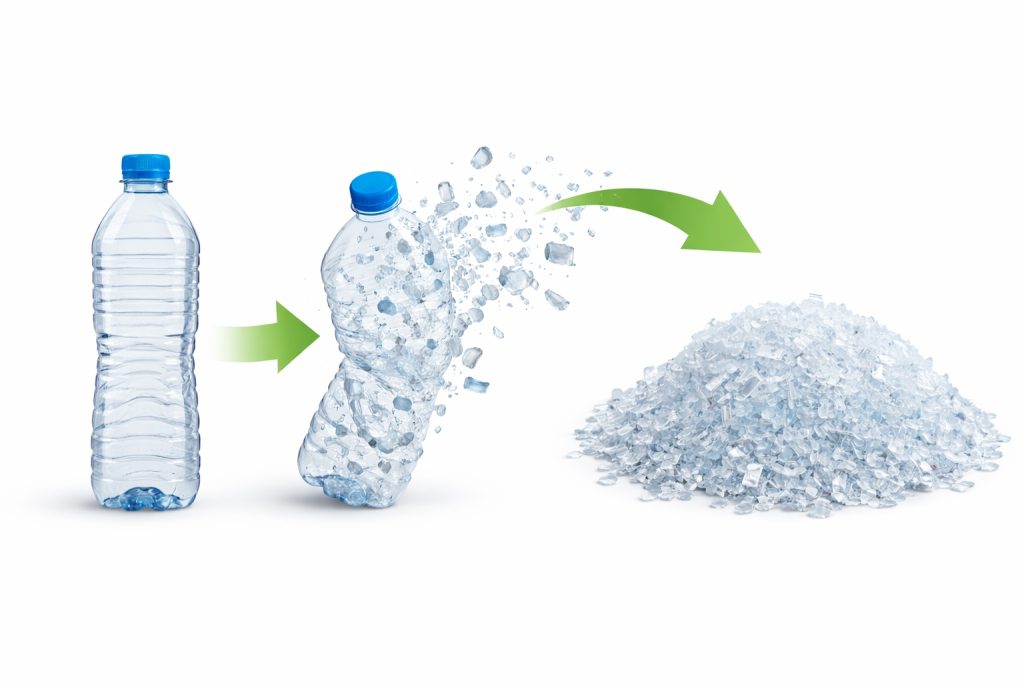
The process of recycling PS pellets involves several key steps, each crucial to transforming waste plastic into valuable new materials. Here’s an in-depth look at the recycling process:
Collection and Sorting: The first step in the recycling process is the collection of PS waste, often sourced from discarded products such as food containers and packaging. Once collected, the waste is sorted to remove any non-PS materials like labels, metals, or other contaminants.
Cleaning and Preprocessing: After sorting, the PS waste is cleaned to remove dirt, oil, or other contaminants. This step ensures that the material is ready for the next stages of recycling. Preprocessing can also involve grinding larger pieces of PS into smaller fragments to make them easier to handle in the next phase.
Shredding and Melting: The cleaned PS waste is then shredded into smaller pieces, which are melted down at high temperatures. This melting process transforms the plastic into a liquid form, ready for the next step.
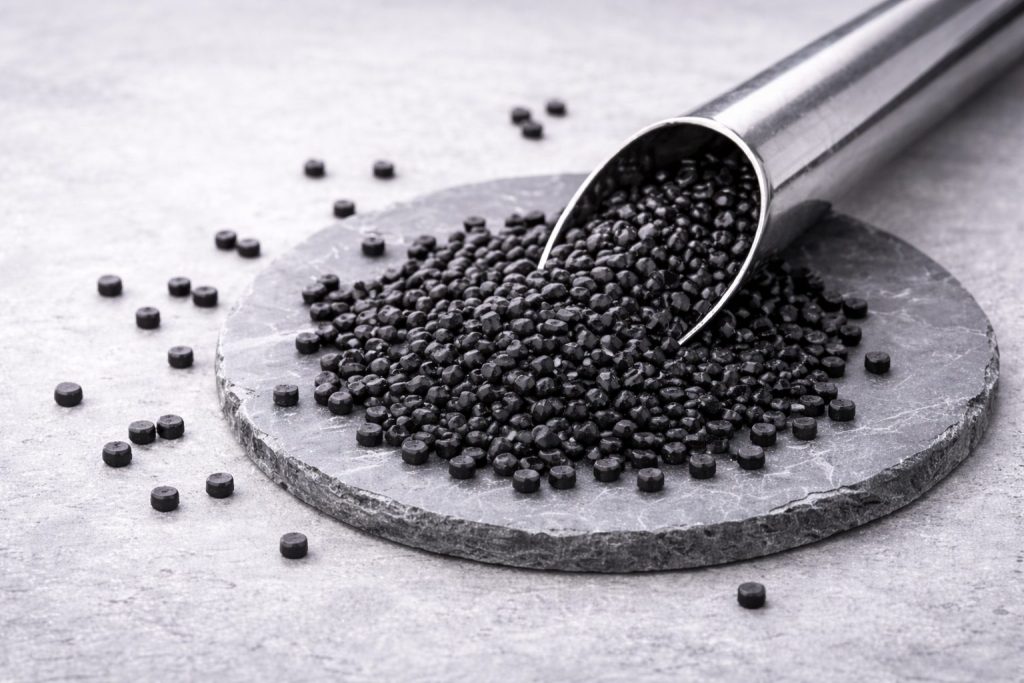
Pelletizing: Once melted, the PS plastic is formed into small pellets through a process called pelletizing. These pellets are uniform in size and can easily be used in manufacturing new products.
Quality Control and Grading: During the pelletizing process, the pellets are carefully inspected for quality. Any defective pellets are removed, and the remaining pellets are graded based on their quality and suitability for various applications.
Final Product Applications: After the pellets are produced and graded, they can be used to manufacture a wide variety of new products. These can include packaging, insulation materials, and consumer goods such as toys and electronics casings.
Economic Benefits of Recycling PS Pellets
Recycling PS pellets offers significant economic advantages for businesses. The cost of raw materials can be a major expense in manufacturing processes, but using recycled PS pellets helps reduce these costs. By recycling waste PS plastic into usable pellets, manufacturers can save money on material procurement.
Additionally, the growing demand for sustainable products has driven up the market for recycled PS pellets. Businesses that incorporate recycled materials into their production processes not only cut costs but also improve their brand image by appealing to eco-conscious consumers.
The recycling of PS pellets also supports a circular economy, where materials are continuously reused, reducing the need for new raw materials and minimizing environmental impact. This can lead to long-term economic sustainability for businesses that adopt recycling practices.
Challenges and Future of Recycling PS Pellets
Despite its numerous benefits, the recycling of PS pellets faces several challenges:
Technological Barriers: The process of cleaning and processing PS waste can be complex and requires advanced technologies. Developing more efficient recycling methods remains a key challenge for the industry.
Regulatory Landscape: The recycling industry is affected by different regulations in various countries, and the lack of standardization can complicate recycling efforts. Governments worldwide are introducing policies aimed at reducing plastic waste, but these policies can sometimes be inconsistent or difficult to implement.
Future Outlook: As technology advances, the process of recycling PS pellets is likely to become more efficient. Innovations such as chemical recycling, which breaks down plastic into its original components, could further improve the recycling of PS and other plastics. Additionally, growing consumer demand for sustainable products will continue to drive the need for recycled materials, ensuring a positive outlook for the future of PS pellet recycling.
Conclusion
Recycling PS pellets not only helps to reduce plastic waste but also provides economic and environmental benefits. By turning waste into value, businesses can contribute to sustainability while saving on raw material costs. The process of recycling PS pellets, from collection to pelletizing, is a critical step in addressing the plastic pollution crisis and promoting a circular economy.